Sophos, a global leader in next-generation cybersecurity, today released findings of a dual ransomware attack where extortion notes left by Karma ransomware operators were encrypted 24 hours later by Conti, another ransomware gang that was in the target’s network at the same time. Sophos details the dual attacks in the article, “Conti and Karma Actors Attack Healthcare Provider at Same Time Through ProxyShell Exploits,” explaining how both operators gained access to the network through an unpatched Microsoft Exchange Server, but then used different tactics to implement their attacks.
“To be hit by a dual ransomware attack is a nightmare scenario for any organization. Across the estimated timeline there was a period of around four days when the Conti and Karma attackers were simultaneously active in the target’s network, moving around each other, downloading and running scripts, installing Cobalt Strike beacons, collecting and exfiltrating data, and more,” said Sean Gallagher, senior threat researcher, Sophos. “Karma deployed the final stage of its attack first, dropping an extortion notice on computers demanding a bitcoin payment in exchange for not publishing stolen data. Then Conti struck, encrypting the target’s data in a more traditional ransomware attack. In a strange twist, the Conti ransomware encrypted Karma’s extortion notes.
“We have seen several cases recently where ransomware affiliates, including affiliates of Conti, used ProxyShell exploits to penetrate targets’ networks. We have also seen examples of multiple actors exploiting the same vulnerability to gain access to a victim. However, very few of those cases involved two ransomware groups simultaneously attacking a target and it shows, literally, how crowded and competitive the ransomware landscape has become.”
The Dual Attack
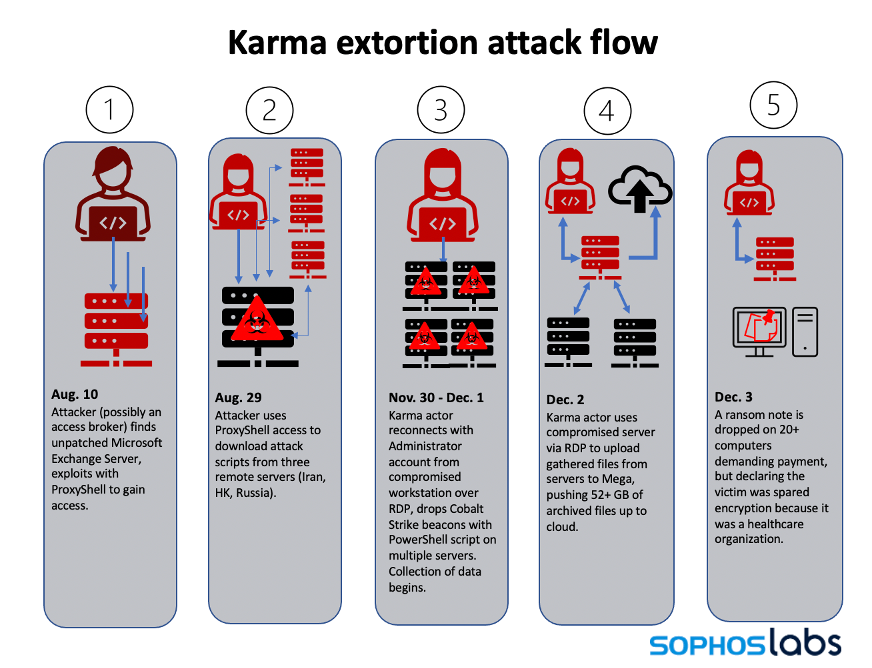
Sophos believes that the first incident started on Aug. 10, 2021, when attackers, possibly Initial Access Brokers, used a ProxyShell exploit to gain access to the network and establish a foothold on the compromised server. The Sophos investigation showed that almost four months passed before Karma appeared on Nov. 30, 2021, and exfiltrated more than 52 gigabytes of data to the cloud.
On Dec. 3, 2021, three things happened:
- The Karma attackers dropped an extortion note on 20 computers, demanding a ransom and explaining that they did not encrypt the data because the target was a healthcare provider
- Conti was quietly operating in the background also exfiltrating data
- The target started onboarding Sophos’ incident response team to help with Karma
While Sophos was onboarding, Conti deployed its ransomware on Dec. 4, 2021. Sophos subsequently tracked the start of the Conti attack to another ProxyShell exploit leveraged on Nov. 25, 2021.

“Whether the initial access broker sold access to two different ransomware affiliates, or whether the vulnerable Exchange server was just an unlucky target for multiple ransomware operators, the fact that a dual attack was possible is a powerful reminder to patch widely known, internet-facing vulnerabilities at the earliest opportunity,” said Gallagher. “Defense-in-depth is vital for identifying and blocking attackers at any stage of the attack chain, while proactive, human-led threat hunting should investigate all potentially suspicious behavior, such as unexpected remote access service logins or the use of legitimate tools outside the normal pattern, as these could be early warning signs of an imminent ransomware attack.”
Sophos endpoint products, such as Intercept X, protect users by detecting the actions and behaviors of ransomware and other attacks, such as those described in this Sophos research.
For further information read the article, “Conti and Karma Actors Attack Healthcare Provider at Same Time Through ProxyShell Exploits.”
.svg?width=185&quality=80&format=auto&cache=true&immutable=true&cache-control=max-age%3D31536000)


.svg?width=13&quality=80&format=auto&cache=true&immutable=true&cache-control=max-age%3D31536000)
